AUTHOR : BABLI
DATE : 9/12/23
Inroduction
In today’s digital economy, credit card[1] processing services are the backbone of most retail businesses, both online and offline. Whether you are a small business owner, an entrepreneur, or a large corporation, accepting credit card payments[2] is a necessity to stay competitive and efficient. In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of credit card processing, from how it works to choosing the right service provider for your business needs.
What is Credit Card Processing?
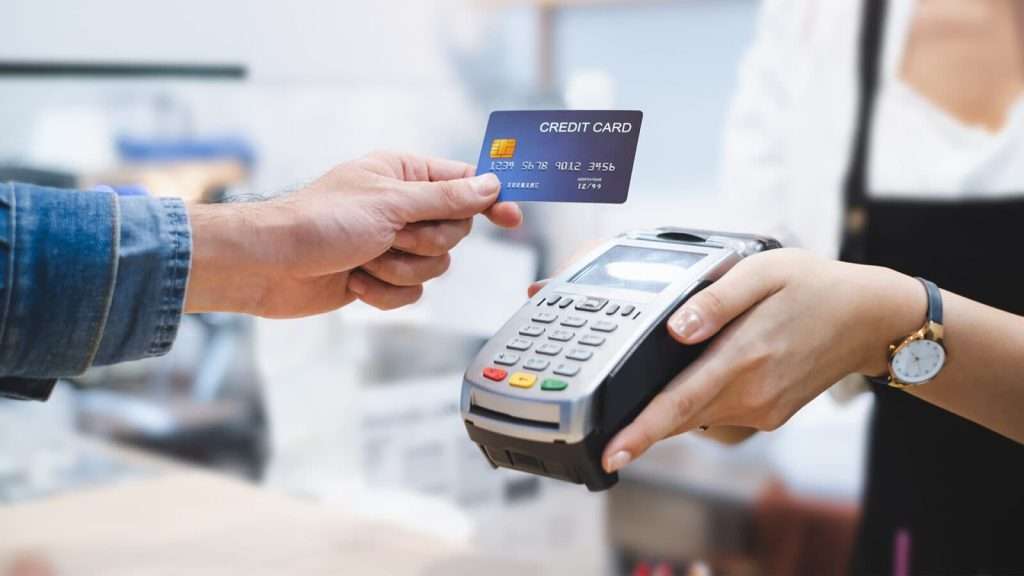

Credit card processing refers to the technology and systems that allow businesses to accept payments made by credit and debit cards[3]. It involves several steps to complete a transaction, ensuring that funds are transferred from the cardholder’s account to the merchant’s account[4] securely and efficiently.
How Credit Card Processing Works
The process of credit card payment encompasses multiple participants and stages, each playing a key role in completing the transaction.
- Authorization: When a customer swipes or enters their credit card information, the merchant sends the transaction request to the payment processor[5]. The payment processor communicates with the card-issuing bank to verify whether the customer has sufficient credit or funds to complete the transaction.
- Authentication: After the issuer bank confirms the transaction, it is either approved or declined based on factors such as available balance, credit limits, and fraud checks.
- Settlement: In the settlement phase, once the transaction is authorized, the payment is deposited into the merchant’s bank account. This procedure usually takes between one to two business days to complete.
Key Players in Credit Card Processing
- Merchant: The merchant is the entity that receives payments via credit card transactions.
- Customer: The person making the payment using their credit card.
- Payment Processor: The intermediary that handles communication between the merchant, the card networks (Visa, MasterCard, etc.), and the issuing bank.
- Acquiring Bank: The merchant’s bank that partners with the payment processor and receives the funds.
- Issuing Bank: The customer’s bank that issued the credit card.
- Card Network: Companies like Visa, MasterCard, American Express, etc., that facilitate the movement of money between the acquiring and issuing banks.
Types of Credit Card Processing Solutions

There are various credit card processing methods and solutions, each suitable for different business models. Choosing the right solution depends on your sales environment (online, in-person, or mobile).
1. Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
A POS system is a physical device (like a terminal or card reader) used by businesses in a brick-and-mortar store. These devices process in-person credit card transactions, whether through a swipe, chip, or contactless payment (NFC). POS systems often come with built-in software that helps with inventory management, sales tracking, and employee management.
2. Online Payment Gateways
For e-commerce businesses, an online payment gateway is essential for securely processing credit card transactions over the internet. These services encrypt and transmit payment data between the customer and the business, allowing for a seamless checkout experience on websites or mobile apps.
3. Mobile Credit Card Processing
Mobile credit card processing services allow businesses to accept payments on-the-go. By using a mobile card reader that connects to a smartphone or tablet, merchants can process credit card transactions anywhere, whether at a pop-up shop, food truck, or a trade show.
Selecting a credit card processing service

When selecting a credit card processing service, there are several factors you should consider to ensure you’re getting the best value for your business:
1. Transaction Fees and Costs
Credit card processors charge fees for each transaction. These fees typically include a percentage of the sale (usually between 1.5% and 3.5%) and a per-transaction fee (often $0.10 to $0.30). Some providers also charge setup fees, monthly fees, and cancellation fees.
It’s important to compare different processors and their pricing structures to ensure you’re getting competitive rates based on your transaction volume.
2. Security Features
Security is a top priority when handling credit card transactions. Look for processors that comply with PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards) regulations. They should also offer features such as tokenization, encryption, and fraud protection to ensure sensitive data is protected.
3. Customer Support
Choose a processor that offers excellent customer support. You should be able to reach someone quickly if an issue arises. Look for 24/7 support, multi-channel communication (phone, email, chat), and a helpful, knowledgeable support team.
Conclusion
Credit card processing is essential for businesses looking to provide seamless, secure payment options to customers. By understanding the different processing solutions available, evaluating factors like fees and security, and choosing a provider that meets your needs, you can ensure a smooth payment experience for your customers and streamline your business operations. Whether you’re running an online store or a physical storefront, selecting the right credit card processor can help you grow your business and enhance customer satisfaction.
FAQs
1. What does PCI compliance entail, and why is it crucial for businesses handling payment information?
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data during and after a transaction. Ensuring PCI compliance is critical for avoiding data breaches and protecting customer trust.
2. How long does it take to receive payments after a credit card transaction?
Typically, it takes between 1 and 2 business days for the funds from a credit card transaction to appear in your merchant account. The timeline for this process varies based on the payment processor and the banks participating in the transaction.
3. Is it possible to accept credit card payments without needing a physical payment terminal?
Yes, you can use online payment gateways, mobile payment solutions, or virtual terminals to process payments without the need for physical hardware.
4. What happens if a credit card transaction is declined?
If a credit card transaction is declined, the payment processor will notify the merchant, and the customer will need to use a different card or payment method.
5. What other payment options are available besides credit cards?
Yes, besides credit cards, businesses can accept digital wallets (like Apple Pay), ACH transfers, cryptocurrency, and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services, depending on the processor.