AUTHOR: SOPHIYA
DATE : 01/11/23
Payment Gateway[1] and Wikipedia are integral components of the modern e-commerce landscape. They serve as the intermediary between an online business and financial institutions, facilitating secure and efficient transactions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Payment Gateway Wikipedia[2], covering their functionality, types, popular providers, benefits, challenges, integration steps, emerging trends, and a glimpse into the future of this vital technology.
How Payment Gateways Work
Understanding the inner workings of Payment Gateway[3] is pivotal for any online business owner. When a customer initiates a transaction on an e-commerce platform, the payment gateway steps in to encrypt the transaction data. This encrypted data is then transmitted to the payment processor[4], which acts as the liaison between the merchant and the customer’s issuing bank. The processor communicates with the bank to authenticate and authorize the payment[5]. Upon approval, the funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
Types of Payment Gateways

Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted Payment Gateway Wikipedia redirect customers to a secure page hosted by the payment gateway provider. Here, customers enter their payment information, which is then processed securely. Examples of hosted portals include PayPal Standard and 2Checkout.
Self-hosted Payment Gateways
Self-hosted portals allow customers to input their payment information directly on the merchant’s website. This provides a seamless checkout experience without redirecting to an external page. Popularly hosted gateways include WooCommerce and Magento.
API-based Payment Gateways
API-based portals integrate directly into the merchant’s website, offering a cohesive and branded checkout experience. This type of gateway, exemplified by Stripe and Braintree, is favored by businesses seeking a high level of customization and control.
Popular Payment Gateway Providers
PayPal
As one of the earliest and most widely recognized payment gateway providers, PayPal boasts a user-friendly interface and extensive global acceptance. It has become a trusted choice for both businesses and consumers alike.
Stripe
Stripe is synonymous with developer-friendly tools and robust security features. It caters to tech-savvy businesses and startups seeking a seamless payment processing solution.
Square
Square offers an all-encompassing solution, combining payment processing with point-of-sale hardware. “It enjoys significant popularity among small enterprises and entrepreneurial ventures.”
Authorize.Net
A pioneer in the Payment Gateway Wikipedia industry, Authorize.Net provides a range of features tailored to businesses of all sizes. Its longevity and reputation make it a reliable choice for many.
Benefits of Using Payment Gateways
Implementing a payment gateway into an e-commerce platform offers a multitude of advantages:
Security
Payment portals utilize sophisticated encryption methods to secure delicate customer data. This ensures that transactions are conducted securely and that financial data remains protected.
Convenience
Payment portals streamline the transaction process, making it quick and hassle-free for customers. “This enhanced user experience can result in augmented conversion rates and heightened customer contentment.”
Global Reach
By accepting payments online, businesses can tap into a global customer base. Portals of Payment facilitate transactions in various currencies, expanding a business’s market reach.
Payment Integration
Payment gateways seamlessly integrate with e-commerce platforms and business software, simplifying operations and enhancing efficiency for merchants.
Challenges in Payment Gateway Integration
Security Concerns
With the rise of cyber threats, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. Businesses must invest in advanced encryption protocols, regular security audits, and stay abreast of industry best practices.
Transaction Fees
Payment gateway providers typically charge transaction fees, which can impact a business’s profit margins. It is crucial to evaluate these costs and factor them into pricing strategies.
Compatibility Issues
Ensuring compatibility with various e-commerce platforms and systems can be a complex task. Thorough testing and integration protocols are necessary to avoid disruptions in the payment process.
Steps to Integrate a Payment Gateway
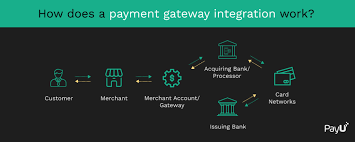
Integrating a payment gateway into an e-commerce website involves several key steps:
- Merchant Account Setup: Establishing a merchant account with a bank or payment processor is the initial step in the integration process.
- Choose a Payment Gateway Provider: Selecting a payment gateway provider that aligns with the business’s needs and preferences is crucial. Consider factors such as transaction fees, security features, and available features.
- API Integration: Once a provider is chosen, integrating their API into the website’s checkout process is the next step. This allows for seamless communication between the website and the payment gateway.
- Testing Transactions: Thoroughly testing the payment gateway is essential to ensure that it functions seamlessly and securely. This includes making test transactions to confirm that the process is functioning as expected.
Emerging Trends in Payment Gateways
Mobile Wallet Integration
The integration of mobile wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay is gaining traction. These wallets offer a convenient and secure method for customers to make payments using their mobile devices.
Cryptocurrency Payments
Some payment gateways are beginning to support cryptocurrency transactions. This caters to the growing interest in digital currencies and provides an additional payment option for tech-savvy consumers.
Biometric Authentication
Advanced security measures such as fingerprint and facial recognition are being integrated into payment processes. This adds an extra layer of security, further safeguarding sensitive financial information.
Future of Payment Gateways
The future of payment gateways looks promising, with innovations in security, convenience, and global accessibility on the horizon. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more seamless and secure payment experiences for both businesses and consumers.
Conclusion
Payment gateways are the backbone of online transactions, ensuring secure and efficient payments. Understanding the different types, providers, and integration steps is crucial for businesses looking to thrive in the digital landscape. By leveraging the benefits of payment portals and staying attuned to emerging trends, businesses can position themselves for success in the ever-evolving world of e-commerce.
FAQs
- What is a payment gateway?
- A payment gateway is a service that authorizes and processes payments for online retailers, brick-and-mortar stores, and e-commerce platforms.
- How do payment gateways work?
- When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway securely captures their payment information, encrypts it, and sends it to the payment processor. The processor then communicates with the customer’s bank to confirm whether the transaction can be approved or declined.
- What are the types of payment gateways?
- There are two main types: hosted payment gateways (redirect customers to a secure page) and integrated payment gateways (allow customers to complete transactions directly on the merchant’s site).
- Are payment gateways secure?
- Yes, reputable payment gateways use advanced encryption and security protocols, such as PCI DSS compliance, to protect sensitive customer data and prevent fraud.
- What fees are associated with payment gateways?
- Payment gateways typically charge transaction fees, which may include a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed fee per transaction. Additional fees may apply for setup, monthly service, and chargebacks.





