AUTHOR : ANNU CHAUHAN
DATE : 25-08-2023
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, efficient payment processing is essential for businesses to provide seamless transactions for their customers. Whether you’re a brick-and-mortar store or an e-commerce giant, understanding the payment processing steps is crucial. This article will walk you through the intricacies of payment processing[1], from initiation to completion.
Introduction
Payment Processing Steps involves a series of intricate steps[2] that ensure a seamless transfer[3] of funds from the customer to the merchant[4]. Each step plays a critical role in the security and also success[5] of the transaction.
Setting Up Your Payment Infrastructure
Before delving into the payment processing steps, it’s crucial to establish a robust payment infrastructure. This includes selecting a payment gateway, partnering with a payment processor, and also ensuring your website’s security measures are up to date.
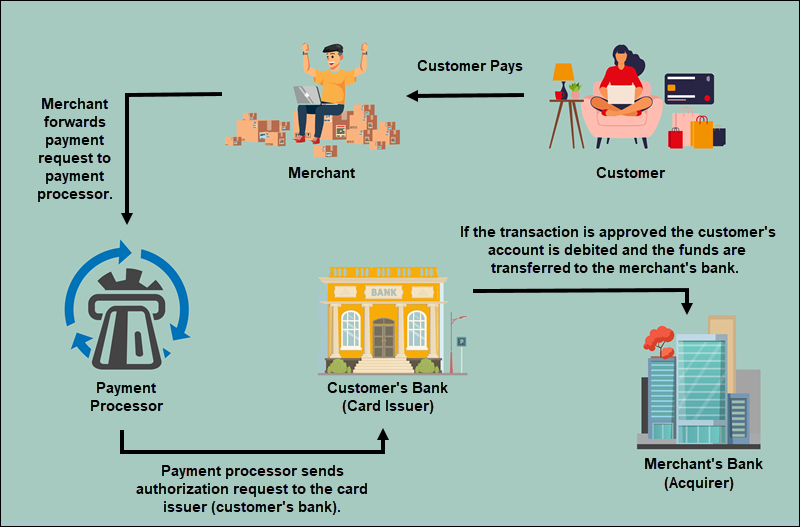
Step 1: Customer Initiates Payment
The payment process begins when a customer decides to make a purchase. This can happen on your website, mobile app, or in-store. The customer adds items to their cart and proceeds to checkout also.
Step 2: Data Encryption and Security also
Once the customer confirms their purchase, they need to encrypt the sensitive payment data, such as credit card information.This ensures that the data remains secure during transmission, safeguarding it from potential cyber threats.
Step 3: Payment Gateway Authorization
The payment gateway then receives the encrypted payment data. The payment gateway acts as an intermediary between the merchant’s website and the payment processor. It authorizes the transaction and conducts preliminary fraud checks.
Step 4: Transmitting the Payment to the Processor
The payment processor facilitates communication between the merchant, the acquiring bank, and also the card associations (like Visa or Mastercard).
Step 5: Payment Processor Routes the Transaction
The payment processor routes the transaction to the appropriate card association. This association communicates with the customer’s issuing bank to get the necessary funds for the purchase.
Step 6: Reaching the Card Association
The card association forwards the transaction to the customer’s issuing bank. This bank evaluates the customer’s account for sufficient funds and also approves or declines the transaction.
Step 7: Issuer Bank Approval
Upon approval, the issuing bank sends an authorization code to the payment processor. This code signifies that the customer has the necessary funds and the transaction can proceed.
Step 8: Transaction Approved or Declined
The payment processor communicates the authorization code to the payment gateway, which informs the merchant whether the transaction is approved or declined.
Step 9: Authorization Response
The customer receives an authorization response. If the payment is approved, the customer’s bank account is earmarked for the transaction amount.
Step 10: Clearing and Settlement
The transaction data goes through clearing and settlement processes, where funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. This involves the interchange of funds between various banks.
Step 11: Fund Transfer Initiation
The acquiring bank initiates the fund transfer to the merchant’s account, ensuring that the merchant receives the payment.
Step 12: Reconciliation of Accounts
Both the merchant and the payment processor reconcile their accounts, ensuring that all transactions are accurately recorded and settled.
Conclusion
In the intricate web of payment processing steps, each stage plays an indispensable role in ensuring a smooth and secure transaction. From customer initiation to fund transfer, the process demands precision, security, and collaboration among various stakeholders.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is a payment gateway? A payment gateway is a technology that securely authorizes and transmits payment data between a merchant and a payment processor.
Q2: How does encryption protect payment data? Encryption converts sensitive payment data into code, making it unreadable to unauthorized users and protecting it from cyber threats.
Q3: What role do card associations play in payment processing? Card associations, like Visa and Mastercard, facilitate communication between merchants, banks, and customers’ issuing banks to ensure smooth transactions.
Q4: What happens if a payment is declined? If a payment is declined, the customer will need to resolve the issue with their bank before the transaction can be completed.
Q5: Why is reconciliation important in payment processing? Reconciliation ensures that both the merchant and the payment processor have accurate records of transactions, minimizing errors and discrepancies.