AUTHOR : BABLI
DATE : 12/12/23
Introduction
Payment[1] transaction processing involves the technologies, techniques, and infrastructure that facilitate the secure transfer of funds in exchange for products or services. The term includes a wide range of activities, such as verifying customer information, completing the transaction, and ensuring the appropriate transfer of funds between the involved parties.
How Payment Transaction Processing Works
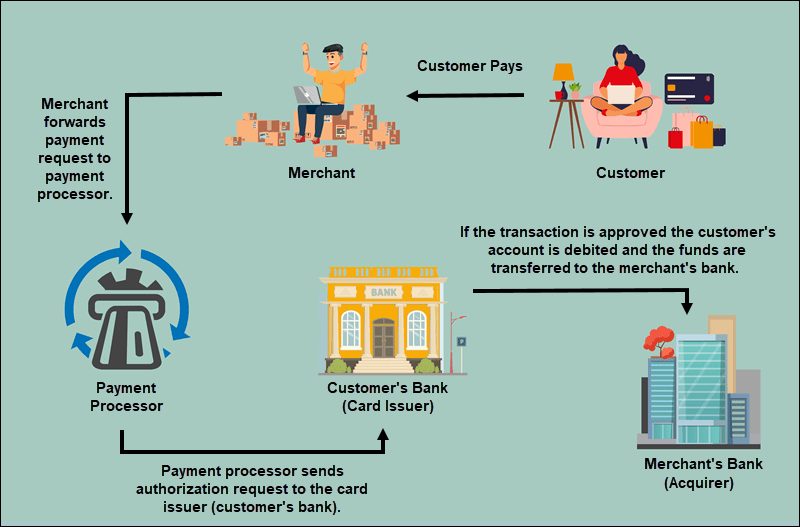
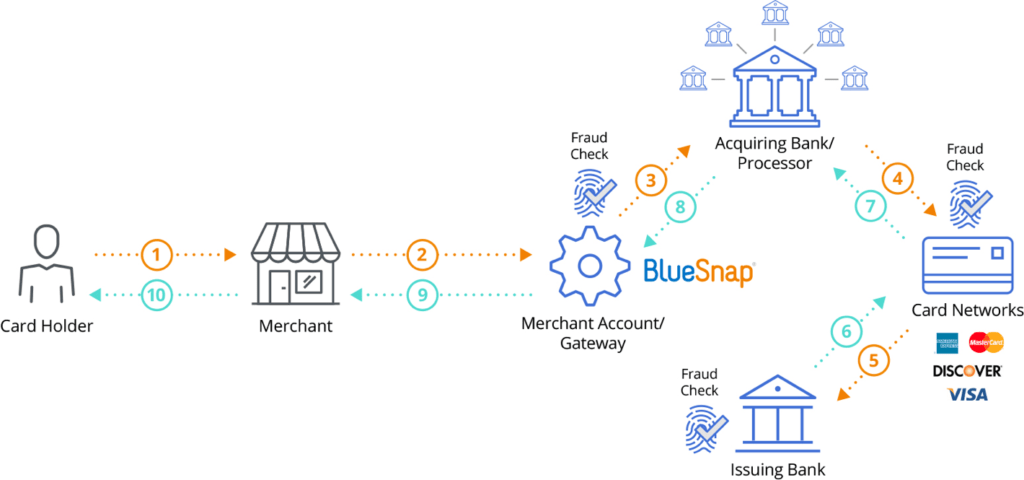
While the process of payment transaction processing[2] can vary depending on the method of payment and the parties involved, the fundamental steps typically remain the same. Here’s a detailed look at how we process payment transactions:
Authorization
Authorization is the initial step in every payment process. This occurs when a merchant[3] requests the payment processor to verify if the customer’s account has enough funds or credit to complete the transaction. The authorization request is typically sent through a secure network to the cardholder’s issuing bank or financial institution[4].
If the funds are available, the system authorizes the payment, and the merchant can proceed to the next step. The transaction will be declined if the account has insufficient funds or any problems are detected with the customer’s account[5].
Authentication
Authentication is the process by which a system verifies the identity of the person initiating a transaction. This can involve entering a PIN, a password, or using biometrics such as fingerprints or facial recognition. In the case of online payments[1], two-factor authentication (2FA) may be used to further secure the transaction.
Settlement
Once the system authorizes and authenticates the payment, the settlement process begins, and the funds move from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. In some cases, the system may briefly store the funds in a “settlement account” before, ultimately, transferring them to the merchant’s bank account.
This process ensures that the merchant receives the agreed-upon amount for the goods or services provided, and it typically takes place within a few days of the initial transaction[2].
Clearing
Clearing is the process where the participating financial institutions exchange payment information to enable the transfer of funds. The clearing process ensures that both the buyer’s and the seller’s banks update their records with the relevant transaction details, such as the amount and the payer’s account information.
Clearing can take place in real-time, especially with modern payment systems like instant payments or digital wallets, or it may take longer depending on the type of transaction (e.g., checks or bank transfers).
Key Players in Payment Transaction Processing
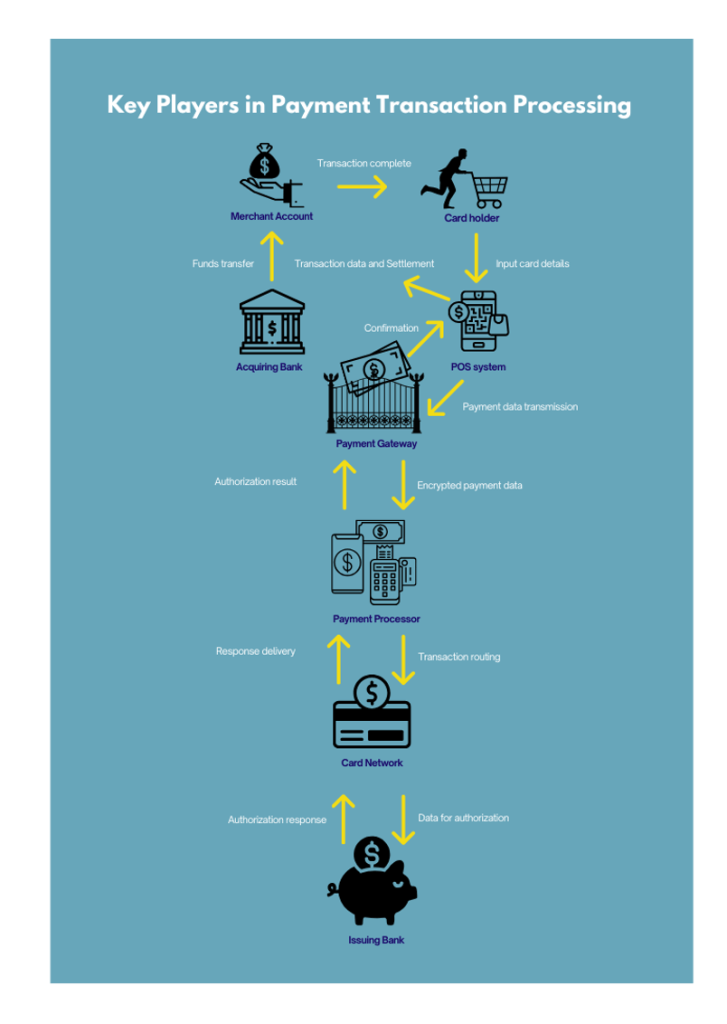
Multiple parties are involved in payment transaction processing[3], each contributing essential functions to the overall process. The key participants in the system are as follows:
Merchant
A merchant is an individual or organization that sells products or services to customers. The merchant initiates the payment transaction and relies on a payment processor[4] or payment gateway to facilitate the transaction. Merchants are responsible for paying processing fees and ensuring they comply with industry regulations.
Customer
The customer is the consumer making a purchase. The payment process starts when the customer submits their payment information, such as credit or debit card details, or opts to use a digital wallet.The customer is also responsible for authorizing the transaction to ensure the payment is legitimate.
Payment Processor
The payment processor is an external service provider responsible for managing the technical execution of a transaction. Payment processors securely transmit payment data between the merchant, customer, and the various financial institutions involved.
Types of Payment Methods

There are several types of payment methods available to consumers and businesses. The most common include:
Credit/Debit Cards
Credit and debit cards remain the most common and established methods of payment for both physical and online purchases. These cards link to the customer’s bank account or credit line and allow them to make payments at physical locations, online stores, and mobile applications.
Digital Wallets
Digital wallets[5], such as PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay, allow customers to store payment information securely and make quick transactions without needing to enter card details each time. Customers can use them for both online and in-store purchases, and they often offer additional layers of security, such as tokenization or biometric authentication.
Bank Transfers
Bank transfers enable individuals to move funds directly between different bank accounts.This payment method is often employed for significant transactions, including rent, mortgages, or business-related payments.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency payments, using digital currencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, are growing in popularity due to their decentralized nature. Blockchain technology typically processes these transactions without the need for traditional financial intermediaries.
Challenges in Payment Transaction Processing
Despite the advancements in payment technology, several challenges persist:
- Security Concerns: Data breaches and fraud are constant threats to payment systems.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements, making it challenging for businesses to stay compliant with global standards.
- Transaction Fees: Payment processors charge transaction fees, which can be costly for small businesses.
- Complexity of Cross-Border Transactions: Currency exchange, varying regulations, and international payment methods can complicate global transactions.
Conclusion
Payment transaction processing is a fundamental element of contemporary commerce, enabling both businesses and consumers to conduct secure and efficient financial exchanges. Understanding the steps involved and the key players in the system helps both merchants and consumers navigate the process with confidence.
FAQs
How do the functions of a payment processor and a payment gateway differ in the transaction process?
A payment processor handles the movement of funds between the merchant and financial institutions, while a payment gateway securely relays the customer’s payment information to the processor.
Why is payment processing security important?
Security in payment processing is crucial because it protects sensitive financial data from theft, fraud, and unauthorized access, ensuring both customers and businesses are protected from financial losses.
Can payment processors charge high fees?
Yes, payment processors typically charge transaction fees, which can vary depending on the volume of transactions and the type of payment method used. Merchants, especially small businesses, can face significant costs from these fees.
What is the typical time required for a payment to be completed and processed?
The processing time for a payment can differ depending on various factors. In most cases, transactions complete within seconds to minutes, but banks may take a few days to settle and clear, especially for larger or international transactions.