AUTHOR : SARIKA U PATHAK
DATE : 11-09-2023
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly reliant on e-commerce to drive revenue and expand their customer base. While this presents countless opportunities, it also exposes companies to various risks[1], including the concept of “high merchant risk[2].” In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of high merchant[3] risk, its implications, and most importantly, how you can safeguard your business against it.High Merchant Risk
Introduction
High merchant[4] risk refers to the level of risk associated[5] with businesses that accept card payments, particularly in the e-commerce sector. It encompasses a wide range of factors, including financial stability, regulatory compliance, and transaction history. Understanding and managing high merchant risk is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of any online business.High Merchant Risk
The Significance of Merchant Risk
Why Does it Matter?
Merchant risk is not a mere technicality; it holds significant implications for businesses of all sizes. High merchant risk can lead to financial losses, damage to reputation, and even legal consequences. By proactively addressing these risks, businesses can protect their bottom line and ensure a positive customer experience.High Merchant Risk
Red Flags and Warning Signs
Identifying high-risk merchants requires a keen eye for detail. Some common red flags include irregular transaction patterns, frequent chargebacks, and a history of regulatory violations. By recognizing these warning signs, businesses can take corrective measures before problems escalate.High Merchant Risk
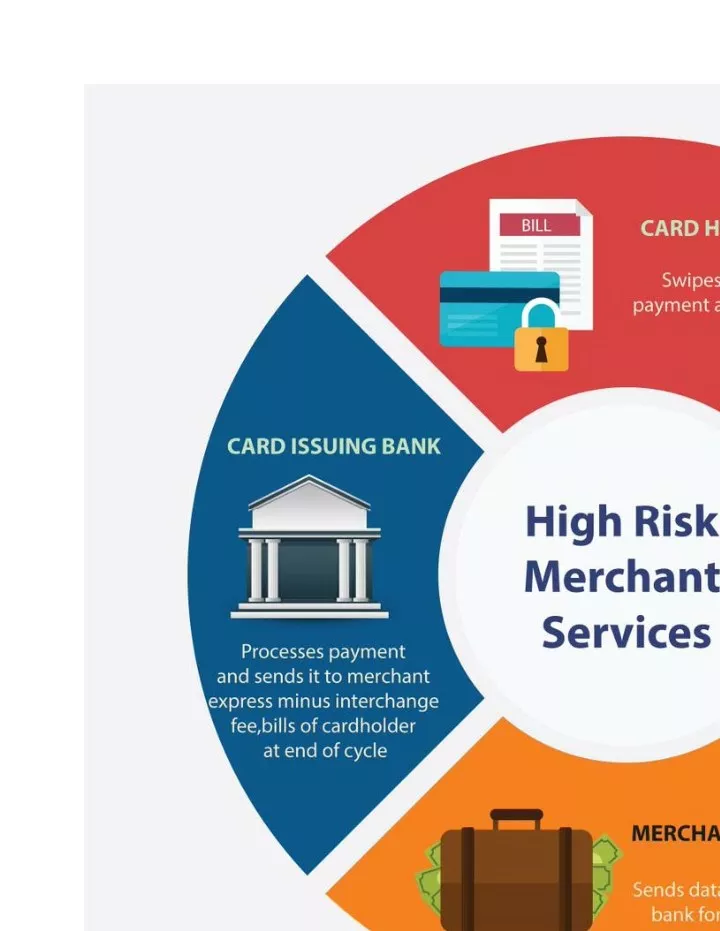
Payment Processors and Chargebacks
Payment processors play a pivotal role in determining a merchant’s risk level. High fees, delayed settlements, and unreliable service can all contribute to elevated risk. Additionally, excessive chargebacks can tarnish a business’s reputation and financial stability.High Merchant Risk
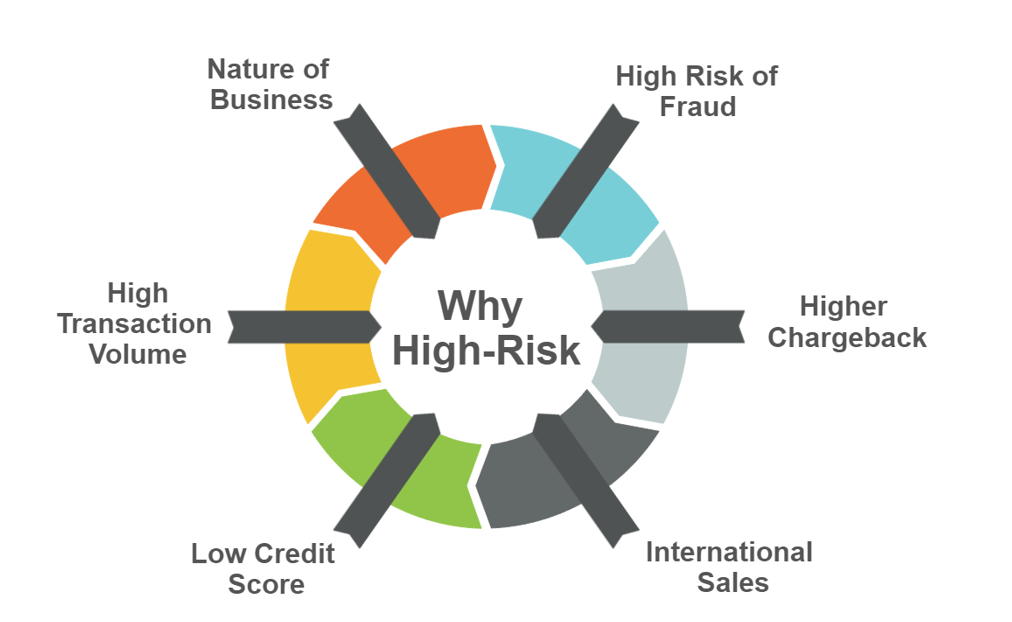
Industry Type and Regulation
Certain industries inherently carry higher risk due to their nature. For example, the adult entertainment or gambling sectors are often considered high risk. Furthermore, varying regulatory requirements add complexity to risk management.
Transaction Volumes
The volume of transactions processed can also impact Rapid growth can strain a business’s financial resources and increase the likelihood of payment processing issues
High merchant risk[1]can result in increased transaction fees, higher chargeback rates, and also difficulty obtaining financing. These financial implications can erode profitability and hinder growth.
Reputation Damage
A tarnished reputation is one of the most significant consequences of high merchant risk. Negative customer reviews, media scrutiny, and social media backlash can harm a business’s brand and also customer trust.
Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
Thorough due diligence is essential for identifying and addressing potential risks also. Conducting risk assessments, reviewing business partners, and staying informed about regulatory changes are all part of effective risk management.
Secure Payment Processing
Choosing a reliable payment processor [2]with a track record of security and efficiency is crucial. Implementing robust fraud detection systems and encryption protocols can further protect against risk.
Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with industry regulations is non-negotiable. Failure to adhere to legal requirements can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage.High
Case Studies
Real-World Examples
To better understand , let’s examine real-world cases where businesses faced significant challenges due to their risk exposure.
Best Practices
Proactive Measures
Prevention is often the best cure when it comes to . Implementing strict internal controls, training staff, and regularly reviewing risk management processes [3]can reduce exposure.
The Role of Technology
AI and Machine Learning in Risk Management
Advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, have revolutionized risk management[4] These tools can analyze vast datasets in real-time to identify anomalies and potential
Future Trends
Emerging Threats and Solutions also
As our digital world continues to transform, so too do the challenges that businesses face in managing understanding high . Stay ahead of the curve by exploring emerging threats and innovative solutions in risk management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, high merchant risk is a critical consideration for businesses engaged in e-commerce. By understanding the factors contributing to risk, implementing proactive measures, and embracing technological advancements, you can protect your business from financial losses and reputational damage.
FAQs
- What exactly is high merchant risk?
- High merchant risk refers to the level of risk associated with businesses that accept card payments, particularly in the e-commerce sector.
- Can small businesses be affected by high merchant risk?
- Yes, high merchant risk can affect businesses of all sizes, including small enterprises. It’s essential for all businesses to assess and manage their risk exposure.
- How do I assess the risk associated with my business?
- Assessing risk involves evaluating factors such as transaction history, industry type, and payment processor performance. Conducting a risk assessment can help identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Are there any industry-specific risks to be aware of?
- Yes, certain industries, such as adult entertainment or gambling, are often considered high risk due to their nature. Understanding industry-specific risks is crucial for effective risk management.
- What are the benefits of investing in risk management technology?
- Investing in risk management technology, including AI and machine learning, can help businesses detect and mitigate risks more effectively, ultimately protecting their bottom line and reputation.





